3. Game Theory
Game Theory
Normal Form Game : for N players if they take actions at the same time.
A normal form game is a tuple
- is a set of number of players
- is an action profile where is the set of actions for playher . Thus, an action profile describes the sumultaneous moves by all players
- is a rewards function that returns an -tuple specifying the payoff each player reveives in state . This is called the utility for an action
A pure strategy for an agent is when the agent selects a single action and plays it. If the agent weere to play the game multiple times, they would choose the same action every time.
A mixed strategy is when an agent selects the action to play based on some probability distribution. That is, we choose action with probabilitu 0.8 and action b with probability 0.2. If the agenty were to play the game an infinite number of times, it would select 80 % of the time and 20 % of the time.
A pure strategy can be treat as a mixed strategy: 100 % probability for one action. That is, a pure strategy is a subset of a mixed stragety
weakly dominant and strongly dominant
A strategy is weakly dominant if the utility received by the agent for playing strategy is greater than or equal to the utility received by that agent for playing
NASH EQUILIBRIA FOR PRISONER’S DILEMMA
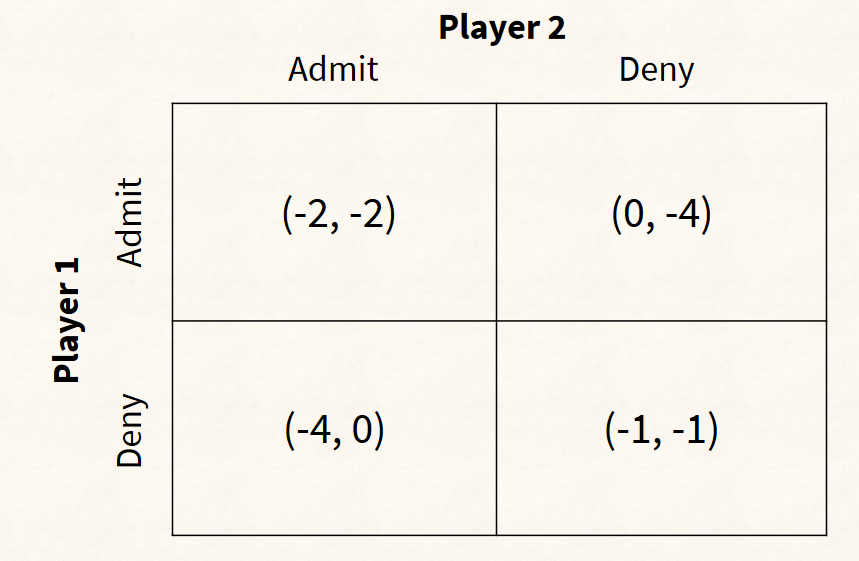
- If player 2 choose Admit, player1 choose admit get greater reward: ; If player 2 choose Deny, player 1 choose Admit receives greater reward.
- If player 1 choose Admit, player2 choose admit get greater reward: ; If player 1 choose Dey, player 2 choose admit get greater reward.
Nash Equilibrium occurs in a game when each player’s strategy maximizes their own payoff, given the strategies chosen by all other players. No player can gain a higher payoff by unilaterally deviating from their current strategy, assuming the other players maintain their strategies.
Nash's existence theorem
Nash proved that if mixed strategies (where a player chooses probabilities of using various pure strategies) are allowed, then every game with a finite number of players in which each player can choose from finitely many pure strategies has at least one Nash equilibrium, which might be a pure strategy for each player or might be a probability distribution over strategies for each player. reference
Key definations recap:
Interleaved action selection (planning) and action execution is known as online planning.