Quantum Phase Estimation
There are some special vectors, called eigenvectors , where applying the X X X eigenvector . For example, ∣ + ⟩ \ket{+} ∣ + ⟩ X X X
X ∣ + ⟩ = ( 0 1 1 0 ) ( 1 2 1 2 ) = ( 1 2 1 2 ) = ∣ + ⟩ \begin{aligned}
X\ket{+} &= \begin{pmatrix} 0 & 1 \\1 &0 \end{pmatrix} \begin{pmatrix} \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}} \\ \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}} \end{pmatrix} \\
&= \begin{pmatrix} \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}} \\ \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}} \end{pmatrix} \\
&= \ket{+}
\end{aligned} X ∣ + ⟩ = ( 0 1 1 0 ) ( 2 1 2 1 ) = ( 2 1 2 1 ) = ∣ + ⟩ The goal of phase estiamtion is:
Given a unitary matrix U U U ∣ ψ ⟩ \ket{\psi} ∣ ψ ⟩ ϕ \phi ϕ U ∣ ψ ⟩ = e i ϕ ∣ ψ ⟩ U\ket{\psi} = e^{i\phi}\ket{\psi} U ∣ ψ ⟩ = e i ϕ ∣ ψ ⟩
Represnting the phase
a 1 2 + a 2 4 + ⋯ + a n 2 n = 0. a 1 a 2 … a n \frac{a_1}{2} + \frac{a_2}{4} + \dots + \frac{a_n}{2^n} = 0.a_1a_2\dots a_n 2 a 1 + 4 a 2 + ⋯ + 2 n a n = 0. a 1 a 2 … a n Shor's algorithm
Period Finding
periodic function
f ( x ) = a x m o d N f(x) = a^x mod N f ( x ) = a x m o d N where a and N are positve integers, a is less than N, and they have no common factors. The period, or order(r r r Smallest (non zero) integer such that:
a r m o d N = 1 a^r mod N = 1 a r m o d N = 1 Shor's solution was to use quantum phase estimation on the unitary operator:
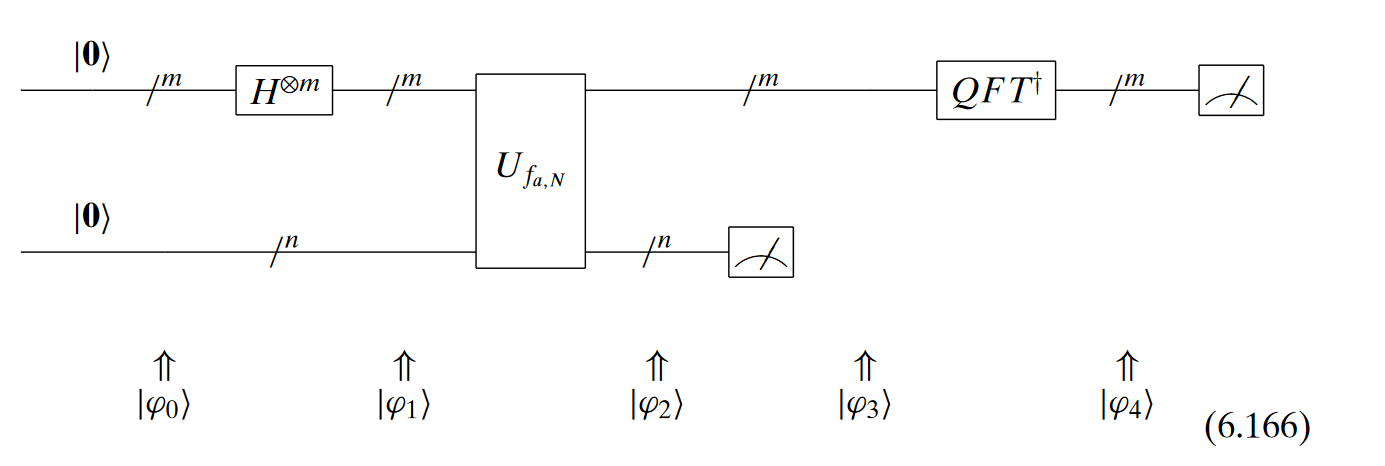
U ∣ y ⟩ ≡ ∣ a y m o d N ⟩ U|y \rangle \equiv |ay \ mod \ N \rangle U ∣ y ⟩ ≡ ∣ a y m o d N ⟩ Shor's Algorithm in quantum circuit
Measurement outcome
Upper register m : outputs binary number to find r
Lower register: n : outputs outcome of f a , N f_{a,N} f a , N
m: outcome M: number of qubits in upper register
k r = m 2 M \frac{k}{r} = \frac{m}{2^M} r k = 2 M m Quantum states during the circuit
∣ ψ 0 ⟩ = ∣ 0 m , 0 n ⟩ |\psi_0 \rangle = |0_m , 0_n \rangle ∣ ψ 0 ⟩ = ∣ 0 m , 0 n ⟩ ∣ ψ 1 ⟩ = ∑ x ∈ { 0 , 1 } m ∣ x , 0 n ⟩ 2 m | \psi_1 \rangle = \frac{\sum_{x \in \{0,1\}^m} |x, 0_n \rangle}{\sqrt{2^m}} ∣ ψ 1 ⟩ = 2 m ∑ x ∈ { 0 , 1 } m ∣ x , 0 n ⟩ ∣ ψ 2 ⟩ = ∑ x ∈ { 0 , 1 } m ∣ x , a x Mod N ⟩ 2 m |\psi_2 \rangle = \frac{\sum_{x \in \{0,1\}^{m}} | x, a^x \text{Mod N} \rangle}{\sqrt{2^m}} ∣ ψ 2 ⟩ = 2 m ∑ x ∈ { 0 , 1 } m ∣ x , a x Mod N ⟩ ·
∣ ψ 3 ⟩ = ∑ j = 0 2 m / r − 1 ∣ t 0 + j r , a x ˉ Mod N ⟩ ⌊ 2 m r ⌋ |\psi_3\rangle = \frac{\sum_{j=0}^{2^m/r - 1} |t_0 + jr, a^{\bar{x}} \, \text{Mod} \, N \rangle}{\left\lfloor \frac{2^m}{r} \right\rfloor}
∣ ψ 3 ⟩ = ⌊ r 2 m ⌋ ∑ j = 0 2 m / r − 1 ∣ t 0 + j r , a x ˉ Mod N ⟩ Example
For N = 15, we will have n = 4 and m = 8. For a = 13, the state ∣ ψ 2 ⟩ |\psi2\rangle ∣ ψ 2 ⟩
∣ 0 , 1 ⟩ + ∣ 1 , 13 ⟩ + ∣ 2 , 4 ⟩ + ∣ 3 , 7 ⟩ + ∣ 4 , 1 ⟩ + ⋯ + ∣ 254 , 4 ⟩ + ∣ 255 , 7 ⟩ 256 \frac{|0, 1\rangle + |1, 13\rangle + |2, 4\rangle + |3, 7\rangle + |4, 1\rangle + \dots + |254, 4\rangle + |255, 7\rangle}{\sqrt{256}} 256 ∣0 , 1 ⟩ + ∣1 , 13 ⟩ + ∣2 , 4 ⟩ + ∣3 , 7 ⟩ + ∣4 , 1 ⟩ + ⋯ + ∣254 , 4 ⟩ + ∣255 , 7 ⟩ After measurement of the bottom qubits, 7 is found
∣ 3 , 7 ⟩ + ∣ 7 , 7 ⟩ + ∣ 11 , 7 ⟩ + ∣ 15 , 7 ⟩ + ⋯ + ∣ 251 , 7 ⟩ + ∣ 255 , 7 ⟩ [ 256 4 ] \frac{|3, 7\rangle + |7, 7\rangle + |11, 7\rangle + |15, 7\rangle + \dots + |251, 7\rangle + |255, 7\rangle}{\left[ \frac{256}{4} \right]} [ 4 256 ] ∣3 , 7 ⟩ + ∣7 , 7 ⟩ + ∣11 , 7 ⟩ + ∣15 , 7 ⟩ + ⋯ + ∣251 , 7 ⟩ + ∣255 , 7 ⟩