QKD and QFT
Quamtum Key Distribution: BB84
In BB84, Alice begins with a bunch of random bits, and for each bit, she randomly chooses either the Z-basis or the X-basis
Bob receives the qubits, and he randomly measures each one in either the Z-basis or X-basis. If the basis he picked was the same as Alice's, then he will get the same result. If he picked the opposite basis, however he will get each possible result with 50% possibility.
Alice and Bob now publicly announce what basis they used for measurement. If they used the same basis, then they know their measurement outcome should agree and they have a shared secret bit. If they used different bases, they will discard these bits.
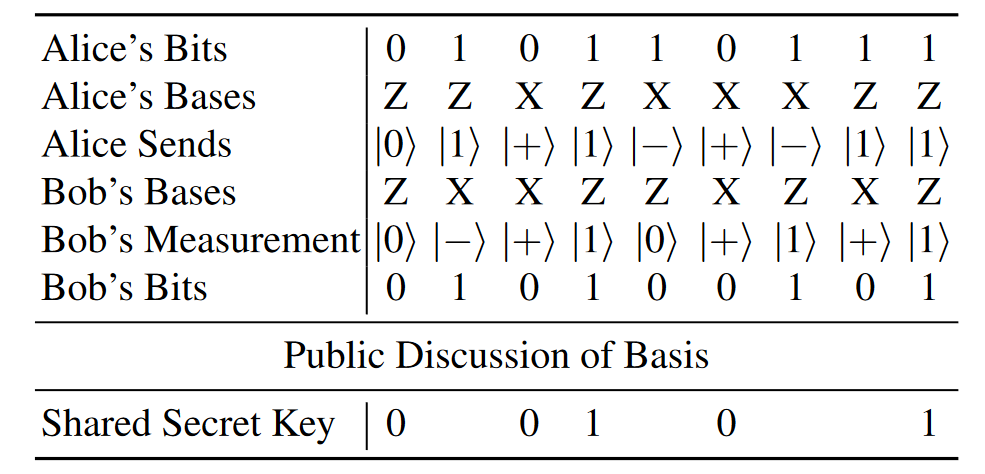
Prevent Eavesdropping
To ensure Eve did not measure the qubits along the way, Alice and Bob can reveal a fraction of their shared qubits.
Generating 306 bits using BB84, revealing 50 bits to ensure no evasdropper.
Thus if Alice and Bob share 50 bits of their shared secre key, the probability that they detect Eve is , which is very close to certainty.
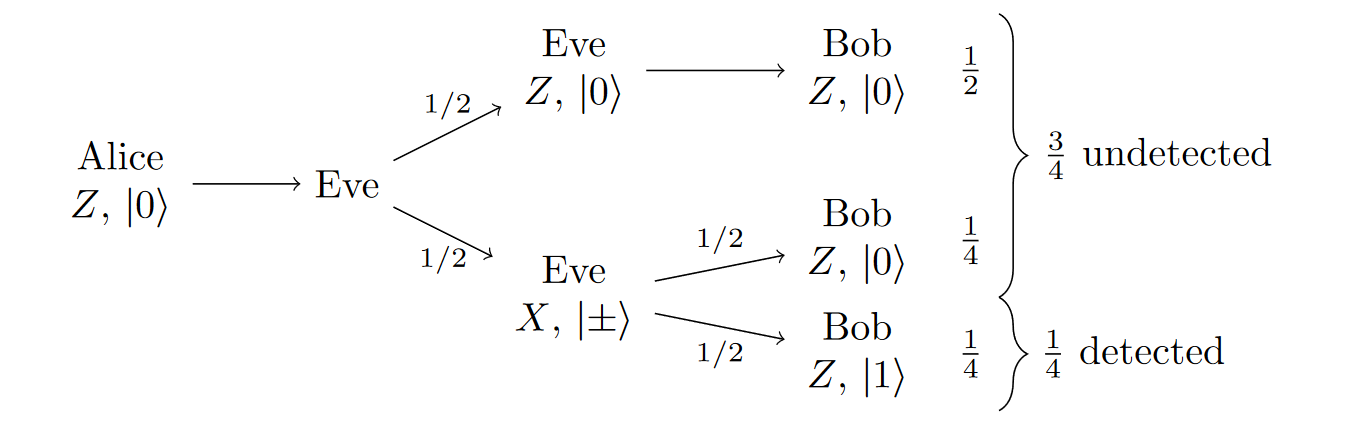
Quantum Fourier Transform
: A normalized quantum state:
Applying the QFT yields another normalized quantum state:
We call the quantum Fourier fransform of . The equat ion:
Generic QFT circuit
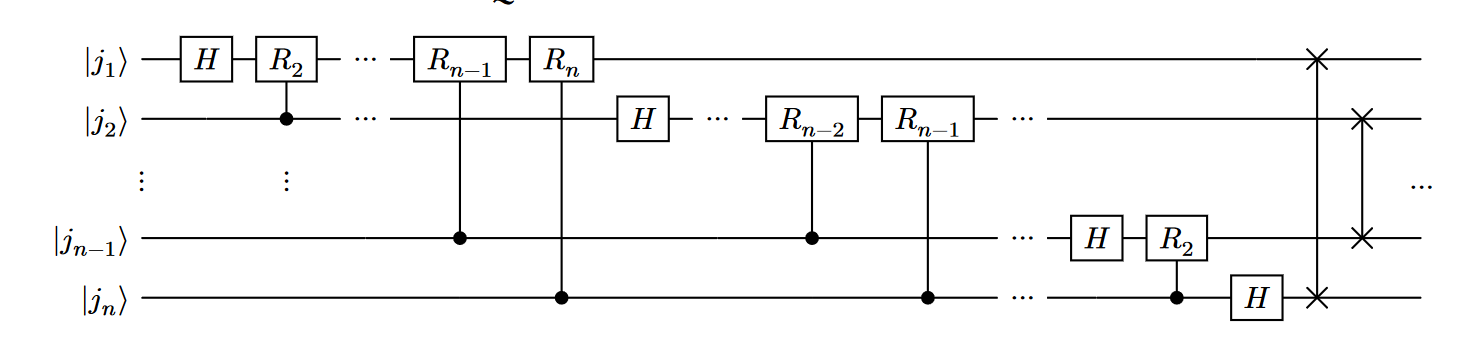 Where :
Where :
To invert the QFT, we must run the circuit in reverse, with the inverse of each gate in place to achieve the transform
Inverse Quantum Fourier Transform
The inverse quantum Fourier transform (IQFT) undoes the QFT.
Since quantum gates are unitary, the inverses are their conjugate transpose.
, and is a rotation about the z-axis of the Bloch sphere by radians.
The :